Starch: Types, Uses, and How to Source Reliable Products from China
Starch is a versatile ingredient widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications. Whether you're a manufacturer or a buyer, understanding the different types of starch and how to source high-quality products is crucial. This guide covers everything you need to know about starch, including its functions, features, and practical applications.
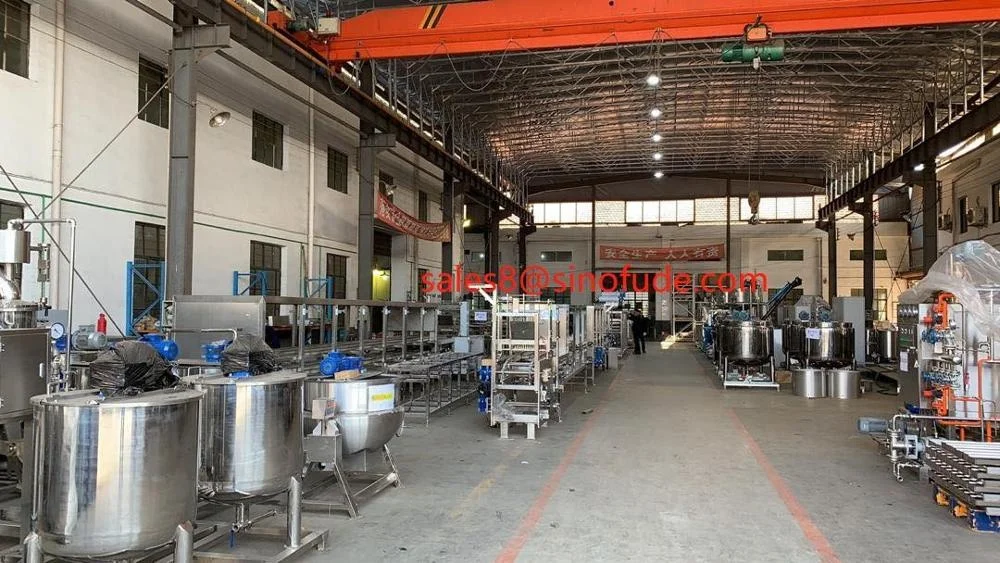
How to Find Reliable Starch from China in 2025
China is one of the largest producers of starch, offering competitive prices and a wide variety of options. To find reliable suppliers, consider the following:
- Certifications: Look for suppliers with ISO, HACCP, or other relevant certifications.
- Sample Testing: Always request samples to test quality before placing bulk orders.
- Supplier Reputation: Check reviews and ratings on platforms like Alibaba to gauge reliability.
- Customization: Some suppliers offer tailored solutions for specific needs, such as modified starch.
What Buyers Should Know Before Buying Starch from China
Purchasing starch from China can be cost-effective, but buyers should be aware of potential challenges:
- Shipping Costs: Factor in logistics expenses, especially for large orders.
- Import Regulations: Ensure compliance with local food safety standards.
- Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs): Some suppliers require large orders, which may not suit small businesses.
- Payment Terms: Negotiate secure payment methods to minimize risks.
Types of Starch
Starch comes in various forms, each with unique properties:
- Corn Starch: Commonly used in food thickening and industrial applications.
- Potato Starch: Ideal for gluten-free recipes and clear gels.
- Tapioca Starch: Popular in Asian cuisine for its chewy texture.
- Wheat Starch: Used in baking and noodle production.
- Modified Starch: Chemically altered for specific industrial uses.
Functions and Features of Starch
Starch serves multiple purposes across industries:
- Thickening Agent: Enhances texture in soups, sauces, and desserts.
- Binding Agent: Holds ingredients together in processed foods.
- Stabilizer: Prevents separation in dairy products and beverages.
- Gelling Agent: Creates firm textures in jellies and candies.
Scenarios of Starch
Starch is used in diverse applications:
- Food Industry: Bakery, confectionery, and dairy products.
- Pharmaceuticals: Tablet binding and coating.
- Textiles: Fabric stiffening and finishing.
- Paper Manufacturing: Improves paper strength and printability.
How to Choose Starch
Selecting the right starch depends on your needs:
- Purpose: Identify whether you need it for food, industrial, or pharmaceutical use.
- Quality: Opt for non-GMO or organic options if required.
- Price: Compare prices but prioritize quality to avoid subpar products.
- Supplier Support: Choose suppliers offering technical assistance and after-sales service.
Starch Q & A
Q: What is the shelf life of starch?
A: Most starches have a shelf life of 12-24 months when stored in a cool, dry place.
Q: Can starch be used in gluten-free products?
A: Yes, starches like potato and tapioca are naturally gluten-free and ideal for such applications.
Q: How do I test starch quality?
A: Conduct viscosity tests or check for impurities under a microscope.
Q: What’s the difference between native and modified starch?
A: Native starch is in its natural form, while modified starch is chemically altered for specific functionalities.
Q: Is starch safe for consumption?
A: Yes, food-grade starch is safe and widely used in culinary applications.